This guide will be a useful tool for starting your own paid advertising campaign. This advertising guide was written for Google Ads but can be easily applied to Microsoft Ads or any other marketing platform.
Although we think that following these steps can be done on your own we understand that creating customer personas, writing great landing pages and advertisement copy, finding effective keywords, designing a landing page, as well as the myriad of other things needed in a campaign can be daunting. The Avalanche Firm is here to guide you through any part of the process!
Step One: The ”GOST” Background & Strategy
Goals
Your goals are a high-level qualitative description of your desired outcome. On the highest level, this reflects your overall company goal. If you are doing a limited scope, for example, a specific digital marketing discipline (Search Engine Optimization, Email Marketing, or PPC) the goal should be a description of how that discipline will contribute to achieving an overall marketing or company goal.
Objectives
These are quantitative outcomes that define your overall goal. What is the specific measure that would indicate success?
Strategy
This is a high-level qualitative description of how you will achieve your goal.
Tactics
These are specific actions that you will take to execute your strategy.
GOST Definitions
| What | How | |
| High-Level | Goals (Qualitative) | Strategy (Qualitative) |
| Detail Level | Objectives (Quantitative) | Tactics (Specific Actions) |
GOST Strategy
| Company Name: |
| GOAL: |
| OBJECTIVE: |
| STRATEGY: |
| TACTICS: |
Step Two: Understanding Your Audience With Personas
Use this persona questionnaire to better understand and define your audience. Use your understanding of the audience for targeting, and the information you receive regarding their pain points to write compelling ad copy.
Please let us know if you would like access to our entire persona survey. This questionnaire goes into more detail and it allows for multiple respondents. Having more people fill out the survey can give your team a better perspective of who your ideal customer really is, what they are looking for, and how to find them.
Persona Question Examples
| Job Title: |
| Job Responsibilities: |
| Educational Background: |
| Average Company Revenue: |
| Career-Level: |
| Age: |
| Primary Job Concerns: |
| Job Pain Points & Challenges: |
| How Do You Solve These Challenges: |
Step Three: Determining Your Budget
Pay-per-click (PPC) gives you lots of control over your budget. Unlike classic forms of advertising like TV, radio, and print which charge you an upfront cost, even if no one visits your website from the advertisements. However, PPC isn’t always cheap. Depending on the competition for keywords, each click can range from only a few cents per click to upwards of $20. Before you set your budget, take a look at Google’s Keyword Planner to see how much each keyword will cost (we’ll cover this in Step Seven: Selecting Your Keywords).
Step Four: Determining The Right Conversion Goals For Your Objectives
What are your objectives?
- Sales
- Leads
- Website Traffic
- Brand Awareness
- Local Store Visits
The way you track conversions is dependent on your objectives. We frequently use leads as a conversion goal. For these campaigns, we would count an online form fill as a successful conversion rather than website traffic or online sales.
Then there are secondary conversions. These are used to help optimize ads by tracking things like time spent on the page or bounce rate. In one account, we noticed that users who stayed on the page for longer than 45 seconds were more likely to convert and fill out the form. So we added a secondary conversion goal of page visits greater than 45 seconds.
Step Five: Time and Location
Make sure your ads only show up where and when you want them to. Your budget could be spent in a matter of minutes with clicks all over the world at all times of the day.
Be aware that you’ll often be tempted to run your campaigns only Monday – Friday. While this may be appropriate, note that in some cases you will see a lower CPC leading to a lower cost/conversion during weekends.
Step Six: Setting Your Bidding Strategy
There are a lot of strategies to choose from and each campaign may require different bidding options. Here are the two most common bidding strategies we use and their definitions:
- Maximize Clicks
An automated bid strategy that sets your bids to help get as many clicks as possible within your budget.
- Maximize Conversions
Sets bids in order to capture the largest number of conversions for the retailer’s budget, based on historical campaign performance and auction data.
Remember, just because Google recommends a specific strategy for you it doesn’t always mean it’s the best option. A good example of this is the Recommendations tab. Here you will see your Optimization score which Google Ads says is an estimation of how well your account is set to perform and to apply the recommendations “to help your campaigns perform better and raise your score.” This isn’t always the case. Although some of the recommendations can absolutely help your account and bottom line, each recommendation should be looked at carefully before approval. Blindly approving can be detrimental to campaign performance.
Step Seven: Selecting Your Keywords
Keyword selection is the foundation of a well-functioning search program. Understand and define where in the funnel you want your campaign to perform, and get to know the keywords that are searched for that funnel position.
3 Keyword Match Types
- Broad Match
This reaches the largest audience and shows up in any search that contains any word from your keyword in any order.
- Phrase Match
Your ad will only appear when your keyword or a close variant of your word appears in the search. Your audience will be smaller but the search terms will be more aligned with your intended keyword.
- Exact Match
Users will only see your ad if they have searched your exact keyword. This is the smallest potential audience but it is more likely that your ad will be what they are looking for.
However, even exact match accounts for searches containing synonyms, plurals, or other very similar variants of the keyword.
Choosing Keywords
Google Keyword Planner
The Google Ads Keyword Planner is a helpful tool for creating powerful keyword lists and getting your PPC campaign off to a good start. The tools for generating keyword ideas and bid predictions in Google Ads are free to use and can help you plan your marketing approach. You may search for keyword and ad group ideas, check how a list of keywords performs, and even combine keyword lists to create new ones with the Google Ads Keyword Tool. It can also assist you in deciding on competitive bids and budgets for your marketing.
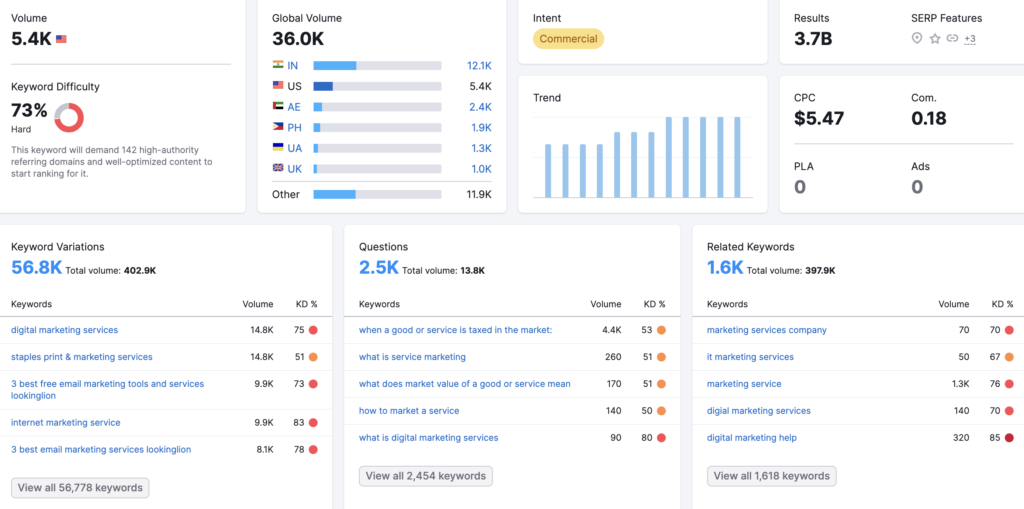
Semrush Keyword Tools
Semrush has similar functionality to the Google Keyword Planner but has much more robust capabilities that go far beyond keyword research.
- Keyword Overview: Search the Semrush database for any keyword. Determine the volume of any keyword on a global and national level, as well as the number of results, intent, CPC, competition level, trend, and more.
- Keyword Manager: Get a more in-depth look at up to hundreds of keywords at once and track changes in SERP (Search Engine Results Page) Features or top competitors.
- Keyword Gap Tool: Compare competitor’s profiles, see where keywords overlap, and find common terms, giving you insight into which keywords would be most effective for your campaigns.
Competitor Research
Take note of paid search results for keywords you think might be relevant. Do the ads sound relevant to your business or are the ads far off from your own offering? The relevance of the ads on prospected keywords is a great tool to see if you should bid on that keyword or if it will be a waste of money.
Negative Keyword Research & Selection
Examining actual user query data based on how people search is one of the most effective techniques to uncover negative keywords. The Google Ads Keyword Planner and Search Terms Report can help you with this.
- Observations from keyword planner
- Look for ads and organic listings that show your keywords that aren’t appropriate.
Quality Score
The Quality Score of a keyword is measured on a scale of one to ten, with one being poor and ten being excellent. The performance of search queries that exactly match your keyword is used to compute your keyword-level score. It’s okay if there are a few highly specific keywords that have a low quality score in an ad group but the ad group keyword list should not generally consist of all low quality score keywords.
Step Eight: Writing Ad Copy
Take a look at your ideal customer personas for your campaign, the GOST strategy, competitor research, as well as influence from the landing page you will be sending your visitors to.
Compelling Copy From Your Persona
Remember your target audience’s character when writing your headline. Who is the audience for your advertisement? What would catch their attention? Review your data once again to make sure you understand your audience persona’s unique interests before writing your headline.
Competitor Research
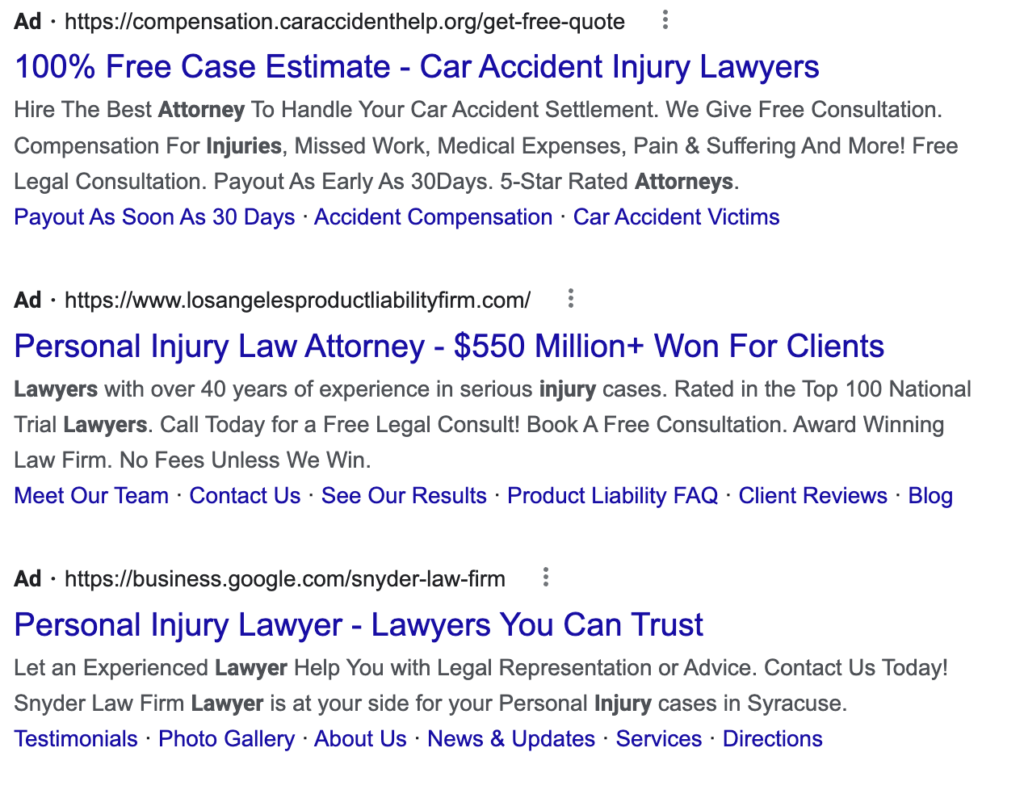
These ads may look similar and we can all agree that plagiarizing is bad but using your competition’s ad copy as an influence on your own is different. That’s why you’re most likely bidding on a similar keyword. More often than not, it’s because your service offerings are similar as well. If all your competitors are offering a free consultation, maybe you should see if you have an offer as or even more enticing than theirs. The great thing about utilizing your own internal data like the persona and GOST technique is that your ad copy has the chance of being unique and resonating better than an advertisement that is written too generically.
Message Matching Your Ad Copy, Keywords, and Landing Pages
Keep in mind that your headlines should reflect what your landing page is actually about. Users will leave immediately if they think your page isn’t relevant to the ad they clicked. That means you paid for an irrelevant click and google just took note that your ad copy and your page didn’t line up which can lower your ad quality score.
Matching the copy of your ads to the copy on your landing page and keywords improves the chances that your visitors will stay on your landing page long enough to complete your call-to-action. There’s a reason why they initially clicked on the ad with that particular copy.
Your Ad Copy Should Address Most Of The Following
- Do you clearly describe your offering?
- Your ad copy and landing page copy is similar.
- Your keywords are included in the ads and landing page.
- You have a good call to action.
- Do you explain what sets you apart from the competition?
- Your ad copy is truthful.
Step Nine: Extensions
Ad extensions offer further details about your business to the main text portion of your ad. Ad extensions are included in everything indicated in the box; they transmit more information about the software, such as product highlights, pertinent links, and pricing. Depending on the context of the search, Google will automatically serve extensions with your ad. Because they match user signals like intent, location, and device, these extra pieces of data in the ad extensions offer value to the user.
Step Ten: Selecting Your Audience
Observation vs. Targeted
When you want to filter your ad group to only show to specified audiences or on specific content that you’ve chosen, use the “Targeting” feature in your ad groups or campaigns. All marketers who run Display advertising should use some sort of targeting.
If you don’t want to narrow your campaign or ad group’s targeting any further but want to see how specific criteria perform with your advertising, use the “Observation” setting.
Choosing Your Audience
- Affinity Audience
Focuses on contacting potential customers in order to raise brand recognition. In some ways, it’s similar to airing a TV commercial for the audience, with the exception that the ads are contextually relevant to the viewer.
- In-Market Audience
Potential clients who are actively researching or looking to buy items and services are targeted by In-Market Audiences. If you want to increase conversions or sales, you should use In-Market Audiences. In-market audiences can also aid remarketing performance by encouraging potential consumers to complete the transaction.
- Custom Audience
Custom audiences select the ideal audience for your campaign based on your campaign’s needs. An MMA company, for example, could prefer to target dedicated jiujitsu practitioners rather than a sports fans affinity demographic. The MMA corporation can specify audiences by:
Enter terms like “grappling,” “bjj athlete,” or “submission wrestling” in the search box.
Using website URLs that provide content about workout regimens, training schedules, nutrition, and other MMA-related topics.
- Remarketing
Remarketing, also known as retargeting, is a common form of digital marketing where companies would show advertisements to users who have visited their website and have either taken or not performed a particular action. It’s a good way to reach out to those who have already shown interest in your business.
Here are some useful remarketing audiences you should consider having as an audience:
- Length Of Site Visit
- Customer Match List
- Blog Readers
- YouTube Viewers
- Abandoned Carts
- Landing Page Visitor
- Product Page Visitor
- Similar To Audience
Google uses a machine-learning algorithm to analyze a source audience (such as a list of website visitors) for shared member attributes, and then it looks for new people who have those traits to identify which individuals “look” the most like an existing audience.
In order to determine a source audience’s browsing activity and the attributes implied by that behavior, Google Ads Display Similar Audiences uses cookie data from users who visit third-party websites in Google’s Display Network. Then, based on their browser history, it searches for others who share characteristics or interests with this source audience and adds them to a similar audience that advertisers can use to target customers with ads.
Step Eleven: Improving Quality Scores
Google rates the quality of your ads, landing pages, and keywords based on the overall user experience on a scale from 1 to 10 when users search for your term. This rating shows how useful your landing page and adverts are to your target audience.
- Expected Click Through Rate (CTR)
This predicts how likely it is for someone to click on your ad when it shows one of your keywords.
- “Average” or “Above Average” – This indicates that there are no serious issues with the projected CTR for your keyword.
- “Below Average” – This indicates that your keyword is predicted to have a low CTR.
- Ad Relevance
This refers to how effectively a keyword suits your ad’s message. When it comes to ad relevance, there are three options: average, above average, or below average.
- Landing Page Experience
When attempting to increase the Quality Score of your keywords, compare them to the copy, or words, on your chosen landing page, as well as the overall user experience of the landing page.
- Is your landing page useful to website visitors from your ad?
- Does your landing page load quickly?
- Is your page easy to read?
- Does your ad copy contain the keywords you’re bidding on?
- Does your ad copy match your landing page?
- Does your landing page have a clear CTA?
Why Is The Quality Score Important
A high score implies that your ad is actually helping a google user find what they’re looking for and that is valuable to Google. A high Quality Score actually lowers your average cost per click compared to ads with a low Quality Score which means a lower cost per conversion.
What a high score means for you:
- Lowers your cost per click which means a lower cost per acquisition.
- Click-through rates are generally higher.
- Higher top-of-page ranking.
The Final Step: Go Get Started!
It takes time to properly market your company, but it may be quite successful. Whether you’re trying to make your first Google Ad campaign or working on improving an existing one, the above-discussed tactics have a proven track record for PPC results. Now that you have the fundamentals to get started and apply these principles to your own project. Just remember that it will take time and understanding to start seeing results.
Good luck!

What’s More Useful Than This Guide?
Get a FREE Marketing Consultation & Custom Plan